In this guide we will show how to install Docker, Docker compose and Redis on a new Linux server. First off, let's do the mandatory update and upgrade before proceeding.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Install some dependencies
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y \
ca-certificates \
curl \
gnupg \
lsb-release
Step 1 Add the key from Docker downloads page
sudo mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | \
sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
2. Setup the Docker Repo
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) \
signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] \
https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
3. Install Docker Engine and Docker Compose V2
Here we want to be sure we are installing the docker compose version , that allows us to do docker compose up , as opposed to docker-compose up, as this is incredibly annoying.
Verify that it was installed correctly
docker --version
![]()
And also we want to verify that docker compose was installed , for some reason the -- flags don't seem to work on this so be sure to typ
docker compose version
![]()
4. Set the Right Permissions for Docker group
Note that for the purposes of this demonstration we are using a sudo user called 'admin' , if you are following along with this post, you will need to change admin to your sudo username which you can find with
whoami
If you have installed Docker and try to run
docker run hello-world
It is likely you will get somethig like the output below
docker: permission denied while trying to connect to the Docker daemon socket at unix:///var/run/docker.sock: Head "http://%2Fvar%2Frun%2Fdocker.sock/_ping": dial unix /var/run/docker.sock: connect: permission denied
Run 'docker run --help' for more information
This just means we need to give docker the right permissions.
Remove need for Sudo on docker commands
Run the command below , replacing admin with your sudo username
sudo usermod -aG docker admin
Add docker group
newgrp docker
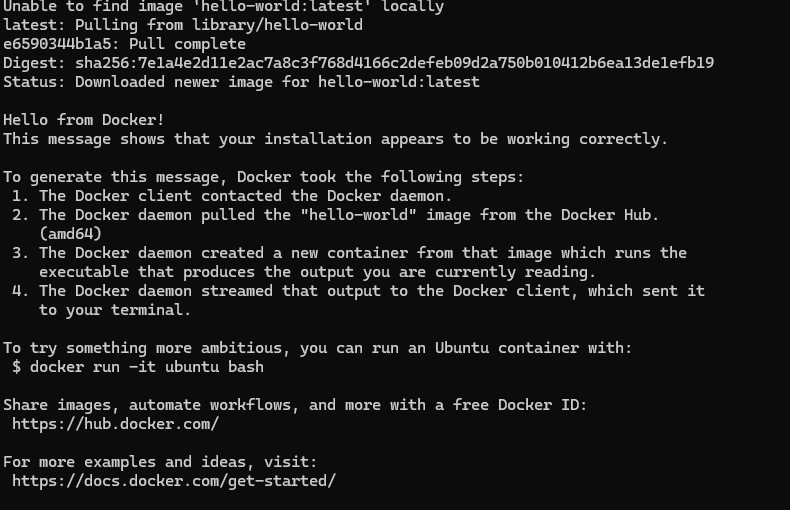
Now, run the hello world again
docker run hello-world
All being well , we should get the output below
And last but not least , it is a good idea to enable Docker to start on boot with the following system d command
sudo systemctl enable docker
Install Redis Docker Image
I personally always use the following image, I am not sure if it is the official image, but comes packed with all the extensions etc
docker pull redislabs/redismod
Now that we have the image downloaded, we probably want to go a little bit slowly to make sure we set up the configuration in the right way, because deleting and starting again, can be a real pain.
Things we need to consider
1) Since we are running Redis on a server, it is likely we may want to connect to it either locally or from another server, so at the very least we want to have a strong password, since we will be required to have an open port to connect from outside the server and don't want someone flushing our keys i.e. deleting all our data, which sounds unlikely, but really isn't :(
2) We need to think about a restart policy , that controls when Redis restarts i.e. on an error etc
3) Since Redis data lives in memory, we probably want to create a docker volume to ensure that data persists even on errors , restarts etc.
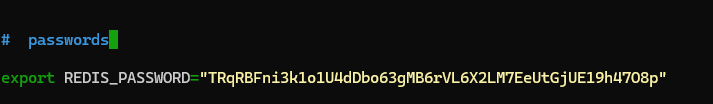
First off , I went and generated a secure password that ended up looking like: TRqRBFni3k1o1U4dDbo63gMB6rVL6X2LM7EeUtGjUE19h47O8p
The next thing I usually do is go to my bashrc file with
sudo nano ~/.bashrc
And then scroll down to the bottom and paste in the following line with your generated password
Make the changes take effect with:
source ~/.bashrc
And then set the correct permissions
chmod 600 ~/.bashrc
Below I share the shell script I use to start redis, you can create it on your server with the command below, I personally usually do this in my home directory, so the redis-data volume we will later create is easily accessible
sudo nano start_redis.sh
And copy in
#!/bin/bash
# Exit immediately if a command fails
set -e
# Check that REDIS_PASSWORD is set
if [ -z "$REDIS_PASSWORD" ]; then
echo "❌ REDIS_PASSWORD environment variable is not set."
echo "Please export it in your shell or .bashrc before running this script."
exit 1
fi
# Optional: create the volume directory if it doesn't exist
mkdir -p "$(pwd)/redis-data"
# Run the Redis container
docker run -d --name redis \
--restart unless-stopped \
--entrypoint "" \
-p 6379:6379 \
-v "$(pwd)/redis-data":/data \
redislabs/redismod \
redis-server --requirepass "$REDIS_PASSWORD" --dir /data
echo "✅ Redis container started with password authentication enabled."
Ensure the script is executablle with
sudo chmod +x start_redis.sh
Before we actually start the container, let's go through what is actually happening in that bash script
--restart unless-stopped : this is the restart policy , it means that this container will restart on errors etc and the only reason for it to stop is if we tell it to.
-p 6379:6379: Here we bind redis to port 6379
-v "$(pwd)/redis-data":/data : This is the volume mount, it will do two things a) create a folder called redis-data in our current working directory (home) and also a folder called data inside the container
-redis-server --requirepass "$REDIS_PASSWORD": This part of the command ensures that we use the password that was saved to our bashrc file.
Let's run the script to get redis running on the server.
./start_redis.sh

And just to double check that redis is actually running, I usually type the following
docker logs redis
And expect to see:
Install Redis CLI
redis-cli is the official command-line interface for interacting with a Redis server. It allows you to connect to a Redis instance and run commands to manage data, configure the server, monitor performance, and debug issues. Especially when working on a remote server, redis-cli really is a must have. Plus it is very easy to install.
sudo apt update && sudo apt install -y redis-tools
If all has been successful, we can connect to the redis instance with
redis-cli -a "$REDIS_PASSWORD"

And that's it, you are ready to start using Redis through a Docker container